Geography
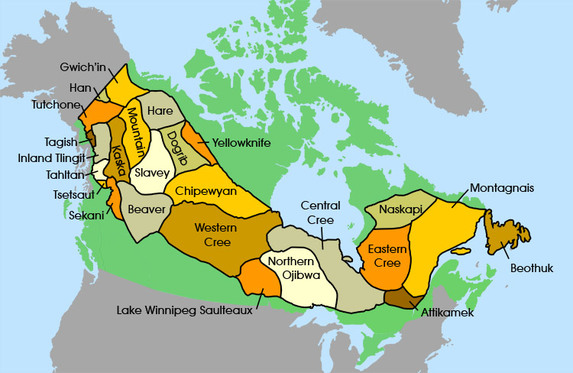
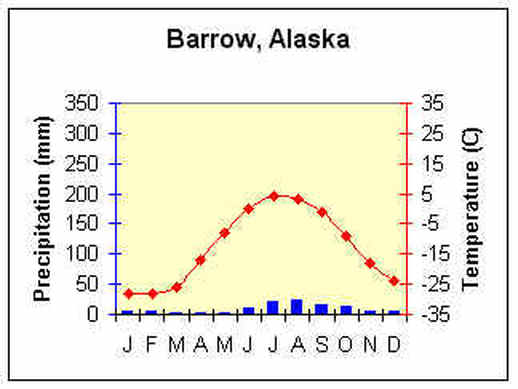
The subarctic region extends from arctic tundra to the mountain, plains, and deciduous forest in the south across the North America, and from Labrador to near Bering Sea. Three quarters of the subarctic region lies in Canadian Shield, Hudson Bay and Mackenzie River lowlands, which has plenty of lakes and rivers. The rest of the land is mountains in plateau and Yukon River lowland. The soil is very poor and swampy and the winters are severe and long. During the winter it snows, which also forms a shelter for people and animals. Summers are short, warm and quite sunny. The temperature varies from -40 degree Celsius to 30 degree Celsius. The type of animals that could be found in the forest was caribou, black bears, moose, and beavers. Since there were lots of lakes and rivers, there were lots of fish as well. Some types of fish were white fish, trout, salmon and pike. The types of trees that could be found were spruce, birch, aspen, cottonwood and pine. Also the subarctic region had very small precipitation. The region also included six provinces and two territories which were Newfoundland and Labrador, Quebec, Ontario, Manitoba, Saskatchewan, Alberta, British Columbia, Yukon, Northwest Territories and most of Alaska as well.